Description
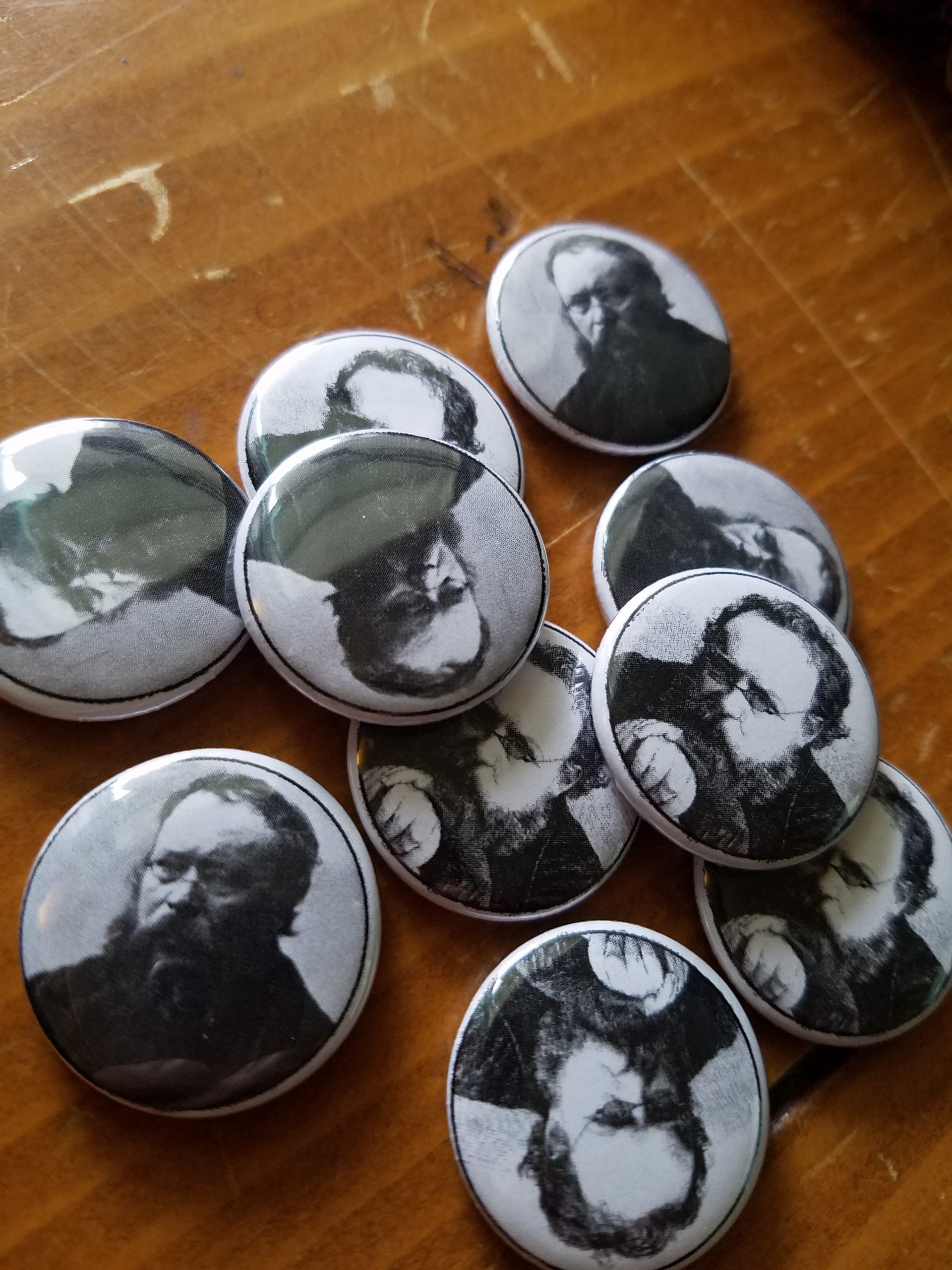
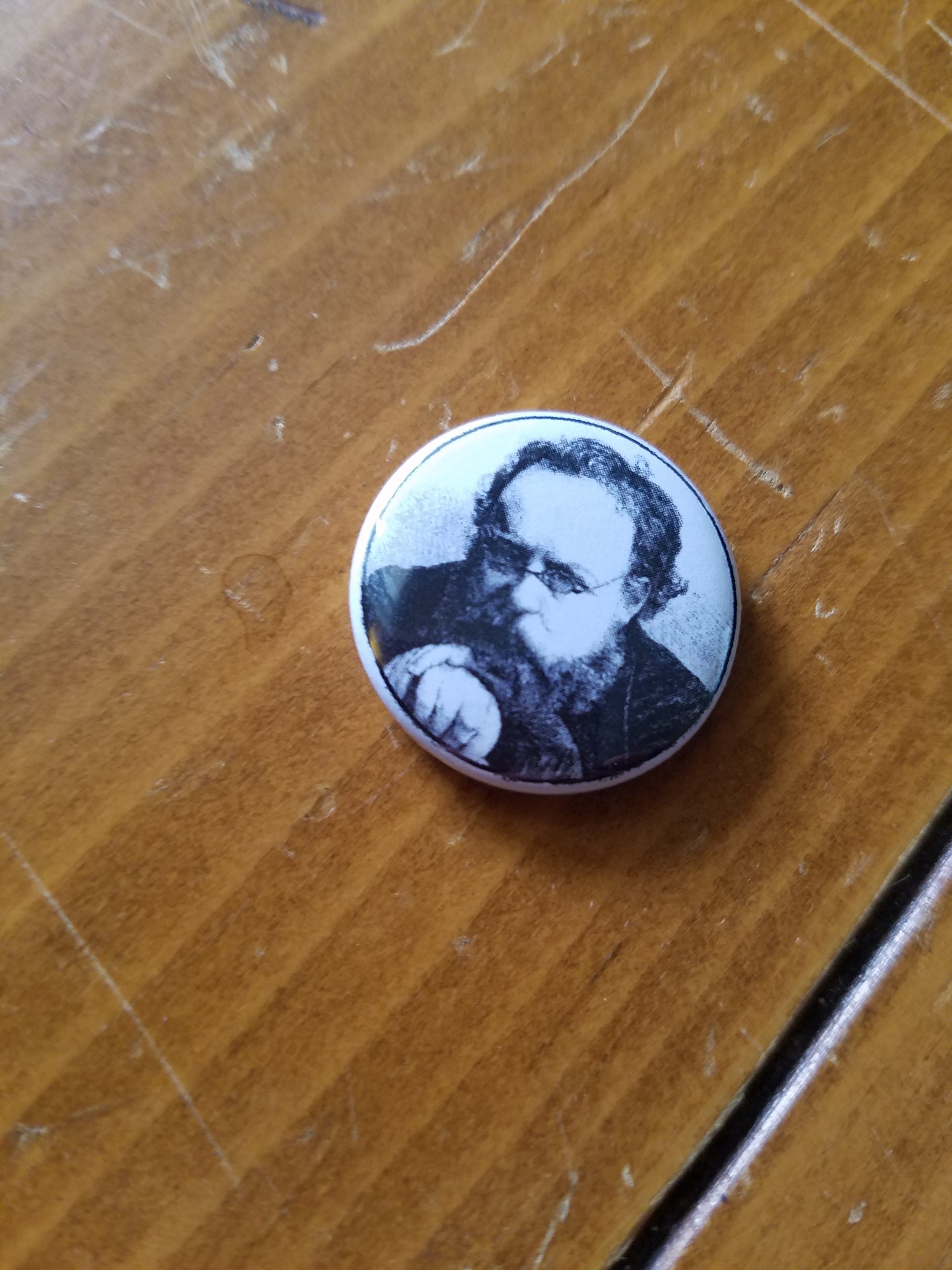
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (UK: /ˈpruːdɒ̃/, US: /pruːˈdɒ̃, pruːˈdoʊn/, French: [pjɛʁ ʒɔzɛf pʁudɔ̃]; 15 January 1809, Besançon – 19 January 1865, Paris) was a French socialist, politician, philosopher, economist and the founder of mutualist philosophy. He was the first person to declare himself an anarchist, using that term and is widely regarded as one of anarchism’s most influential theorists. Proudhon is considered by many to be the “father of anarchism”. Proudhon became a member of the French Parliament after the Revolution of 1848, whereafter he referred to himself as a federalist.[12] Proudhon described the liberty he pursued as “the synthesis of communism and property“. Some consider his mutualism to be part of individualist anarchism while others regard it to be part of social anarchism.
Proudhon, who was born in Besançon, was a printer who taught himself Latin in order to better print books in the language. His best-known assertion is that “property is theft!“, contained in his first major work, What Is Property? Or, an Inquiry into the Principle of Right and Government (Qu’est-ce que la propriété? Recherche sur le principe du droit et du gouvernement), published in 1840. The book’s publication attracted the attention of the French authorities. It also attracted the scrutiny of Karl Marx, who started a correspondence with its author. The two influenced each other and they met in Paris while Marx was exiled there. Their friendship finally ended when Marx responded to Proudhon’s The System of Economic Contradictions, or The Philosophy of Poverty with the provocatively titled The Poverty of Philosophy. The dispute became one of the sources of the split between the anarchist and Marxist wings of the International Working Men’s Association. Some such as Edmund Wilson have contended that Marx’s attack on Proudhon had its origin in the latter’s defense of Karl Grün, whom Marx bitterly disliked, but who had been preparing translations of Proudhon’s work.
Proudhon favored workers’ council and associations or cooperatives as well as individual worker/peasant possession over private ownership or the nationalization of land and workplaces. He considered social revolution to be achievable in a peaceful manner. In The Confessions of a Revolutionary, Proudhon asserted that “Anarchy is Order Without Power”, the phrase which much later inspired in the view of some the anarchist circled-A symbol, today “one of the most common graffiti on the urban landscape”. Proudhon unsuccessfully tried to create a national bank, to be funded by what became an abortive attempt at an income tax on capitalists and shareholders. Similar in some respects to a credit union, it would have given interest-free loans. After the death of his follower Mikhail Bakunin, Proudhon’s libertarian socialism diverged into individualist anarchism, collectivist anarchism, anarcho-communism and anarcho-syndicalism, with notable proponents such as Carlo Cafiero, Joseph Déjacque, Peter Kropotkin and Benjamin Tucker. (wikipedia)
Collection of written works (The Anarchist Library)